Custom PT100 temperature sensor manufacturer in China
What is a PT100 Temperature Sensor?
The PT100 temperature sensor is a widely used industrial temperature measurement device that converts temperature variations into standardized output signals. Its core component is a platinum-based resistance element, which exhibits a predictable and stable resistance-temperature relationship. Here's a detailed overview:
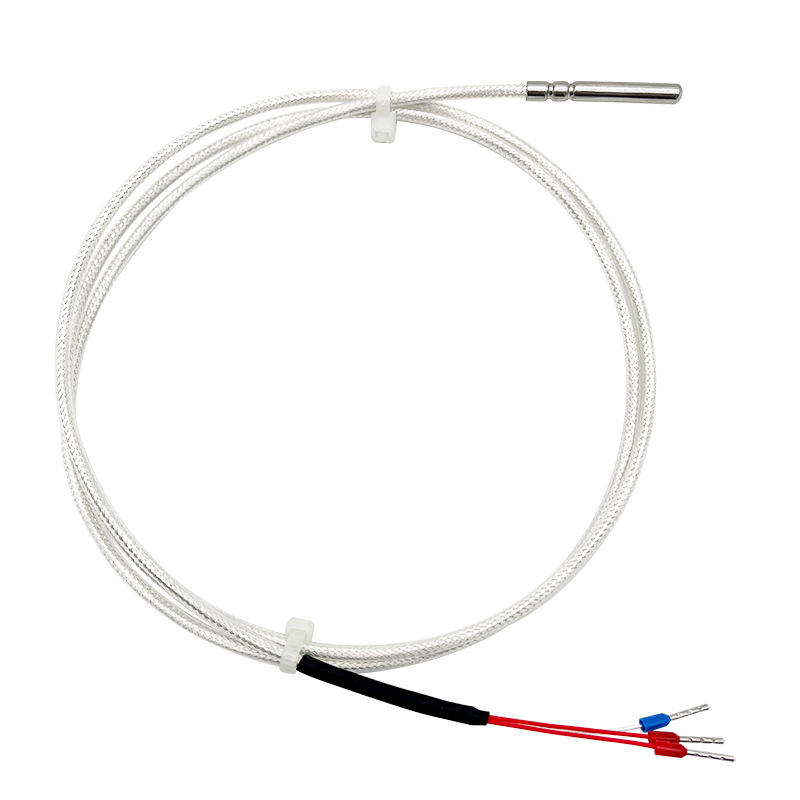

Basic Principle
Material: "PT" stands for platinum (Platinum), a noble metal known for its chemical stability and high-temperature resistance.
Resistance Value: "100" indicates the sensor's resistance at 0°C (100 ohms). As temperature rises, the resistance increases linearly (approximately 0.385 Ω/°C).
Measurement Range: The sensor operates effectively from -200°C to +850°C, covering most industrial and environmental applications.
Working Mechanism
Resistance-Temperature Relationship: The sensor's resistance changes proportionally with temperature, following the formula:

Signal Conversion: To measure resistance, the sensor requires a constant current source. A signal converter (often integrated into a transmitter) processes the resistance into a standardized output (e.g., 4–20 mA or digital signals) for easy integration into control systems.
Key Features
High Accuracy: Meets IEC 60751 standards, with accuracy classes like ±0.15°C (A-grade) or ±0.30°C (B-grade).
Stability: Platinum's inertness ensures long-term reliability with minimal drift.
Wide Applicability: Suitable for harsh environments due to robust construction (e.g., stainless steel or ceramic housing).
Common Applications
Industrial Automation: Monitoring machinery temperatures in manufacturing plants.
Medical Devices: Ensuring precise temperature control in diagnostic equipment.
HVAC Systems: Regulating heating and cooling in buildings.
Aerospace: Measuring critical temperatures in aircraft components.
Installation Considerations
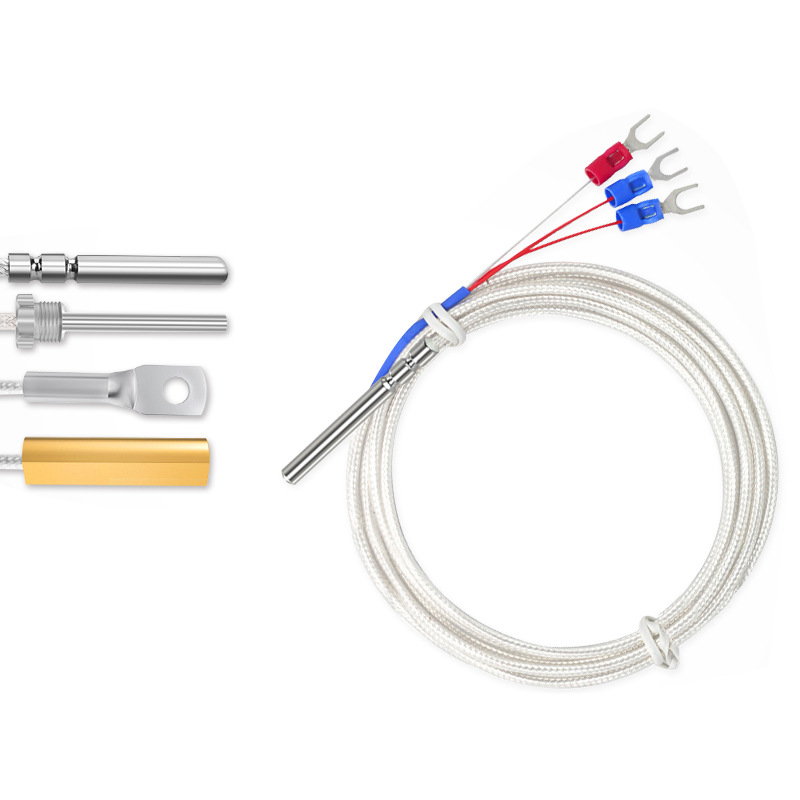
Wiring Methods: Typically uses a three-wire or four-wire configuration to eliminate errors caused by lead resistance.
Calibration: Regular calibration is recommended to maintain accuracy over time.

Understanding PT100 Temperature Sensor Wiring Configurations: 2-Wire, 3-Wire, and 4-Wire
PT100 temperature sensors are widely used for precise temperature measurement due to their stability and accuracy. The choice between 2-wire, 3-wire, and 4-wire configurations significantly impacts measurement accuracy, especially in industrial applications. This article explains the differences and provides guidance on selecting the appropriate wiring scheme.
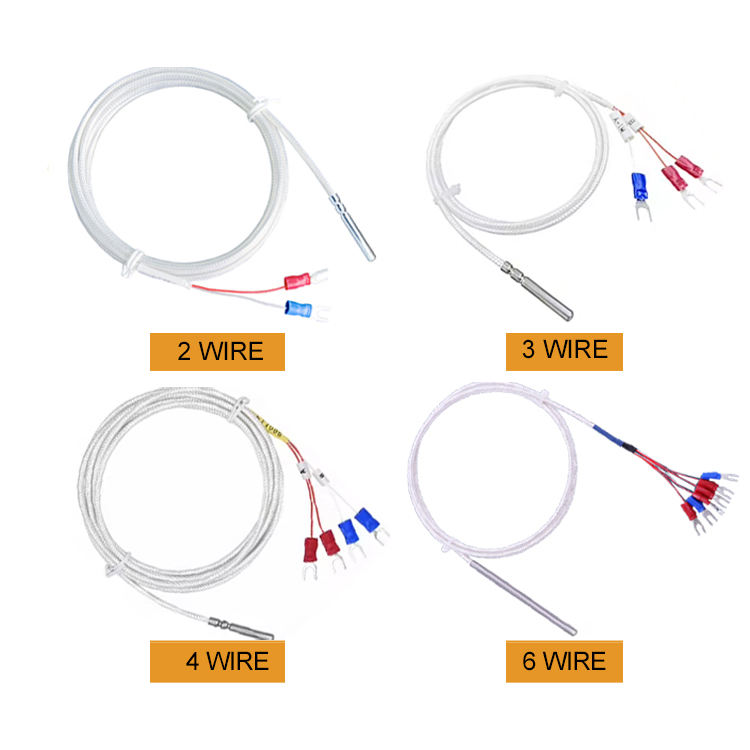

PT100 2-Wire Configuration
Description: Simplest form, where two wires supply power and carry the measurement signal simultaneously.
Advantages: Low cost, easy wiring, and minimal installation complexity.
Limitations: Susceptible to errors caused by lead resistance (RLEAD), which can distort readings over long distances or in high-precision scenarios.
Best Suited For: Short-distance applications where cost is prioritized over accuracy, such as basic HVAC systems or local monitoring.
PT100 3-Wire Configuration
Description: Uses three wires, with one dedicated to canceling lead resistance errors. A bridge circuit or matched current source ensures compensation.
Advantages: Balances cost and accuracy by mitigating RLEAD effects, making it the most common choice in industrial process control.
Limitations: Requires matched lead resistances (RLEAD1 = RLEAD2) for optimal performance.
Best Suited For: General-purpose applications like manufacturing, automotive, and energy sectors where moderate accuracy is sufficient.
PT100 4-Wire Configuration (Kelvin Connection)
Description: Employs four wires—two for power and two for measurement—fully isolating the signal from lead resistance.
Advantages: Highest accuracy, as it eliminates RLEAD entirely, ideal for laboratory-grade or critical systems.
Limitations: Higher cost and more complex wiring due to additional connections.
Best Suited For: High-precision environments such as medical devices, calibration labs, or advanced research.
How to Choose the Right PT100 Sensor
Selecting the appropriate wiring configuration depends on your application’s requirements:
- Prioritize Cost-Effectiveness: Use 2-wire for non-critical short-range monitoring.
- Balance Performance and Budget: Opt for 3-wire in industrial settings where lead resistance compensation is essential.
- Demand Maximum Accuracy: Deploy 4-wire for systems where measurement integrity is paramount, such as in scientific instruments.
- By understanding these wiring differences, you can optimize PT100 sensor performance for your specific temperature measurement needs.
In summary, the PT100 sensor is a cornerstone of temperature measurement due to its precision, durability, and versatility. Its design and performance make it indispensable across diverse industries where reliable temperature data is essential.